Investing in the stock market can be a rewarding journey towards financial freedom, but it’s not without its risks. For the uninitiated, the world of stocks can seem daunting and complex. However, with the right knowledge and strategies, anyone can become a successful investor. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fundamentals of stock market investment, exploring various strategies, understanding risks, and unlocking the potential rewards.
Understanding the Stock Market
At its core, the stock market is a place where investors buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. These shares represent ownership in the company, and their value fluctuates based on various factors such as company performance, market conditions, and investor sentiment.
Stocks are traded on stock exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq, where buyers and sellers come together to trade shares. Investors can buy stocks through brokerage firms, which act as intermediaries between the investor and the stock market.
Types of Stocks
Stocks can be classified into various categories based on different criteria. Common classifications include:
Blue-chip stocks
Blue-chip stocks represent shares of large, well-established companies with a proven track record of stable performance and consistent dividends. These companies are typically leaders in their respective industries and have a strong competitive advantage. Examples of blue-chip stocks include:
- Apple Inc. (AAPL): One of the world’s largest technology companies, known for its iPhone, iPad, and Mac products.
- Microsoft Corporation (MSFT): A global leader in software, cloud computing, and technology solutions.
- The Coca-Cola Company (KO): A multinational beverage corporation known for its iconic soft drink brands.
- Johnson & Johnson (JNJ): A diversified healthcare company engaged in pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and consumer health products.
- Procter & Gamble Company (PG): A consumer goods giant with a portfolio of well-known brands, including Pampers, Tide, and Gillette.
Growth stocks
Growth stocks belong to companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to other companies in the market. These companies typically reinvest their profits back into the business to fuel expansion and innovation, rather than paying out dividends. Examples of growth stocks include:
- Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN): A multinational technology company known for its e-commerce, cloud computing, and digital streaming services.
- Tesla, Inc. (TSLA): A leading electric vehicle manufacturer and renewable energy company.
- Netflix, Inc. (NFLX): A subscription-based streaming service offering a wide range of movies, TV shows, and original content.
- Shopify Inc. (SHOP): A Canadian e-commerce company that provides a platform for online stores and retail point-of-sale systems.
- NVIDIA Corporation (NVDA): A semiconductor company specializing in graphics processing units (GPUs) for gaming, artificial intelligence, and data centers.
Value stocks
Value stocks are shares of companies that are considered undervalued by the market, trading at a lower price relative to their intrinsic value. Value investors seek out these stocks with the expectation that their true worth will be recognized over time. Examples of value stocks include:
- Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (BRK.A / BRK.B): A multinational conglomerate led by renowned investor Warren Buffett, with diverse holdings in various industries.
- Exxon Mobil Corporation (XOM): A multinational oil and gas company engaged in exploration, production, refining, and marketing of energy products.
- AT&T Inc. (T): A telecommunications company providing wireless, internet, and entertainment services.
- Bank of America Corporation (BAC): One of the largest banking and financial services companies in the United States.
- General Motors Company (GM): A multinational automotive corporation producing vehicles under various brands, including Chevrolet, GMC, and Cadillac.
Dividend stocks
Dividend stocks are shares of companies that pay regular dividends to shareholders, providing a steady income stream. These companies typically have a stable financial position and generate consistent cash flow. Examples of dividend stocks include:
- Johnson & Johnson (JNJ): A diversified healthcare company known for its pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and consumer health products.
- The Procter & Gamble Company (PG): A consumer goods giant with a portfolio of household and personal care brands.
- Coca-Cola Company (KO): A multinational beverage corporation known for its soft drink brands.
- Verizon Communications Inc. (VZ): A telecommunications company providing wireless, internet, and television services.
- Pfizer Inc. (PFE): A pharmaceutical company engaged in the development and production of prescription drugs and vaccines.
By understanding the characteristics and examples of each type of stock, investors can tailor their investment strategies to meet their financial goals and risk tolerance. Whether seeking capital appreciation, income generation, or a combination of both, diversifying across different types of stocks can help investors build a resilient and well-balanced investment portfolio.
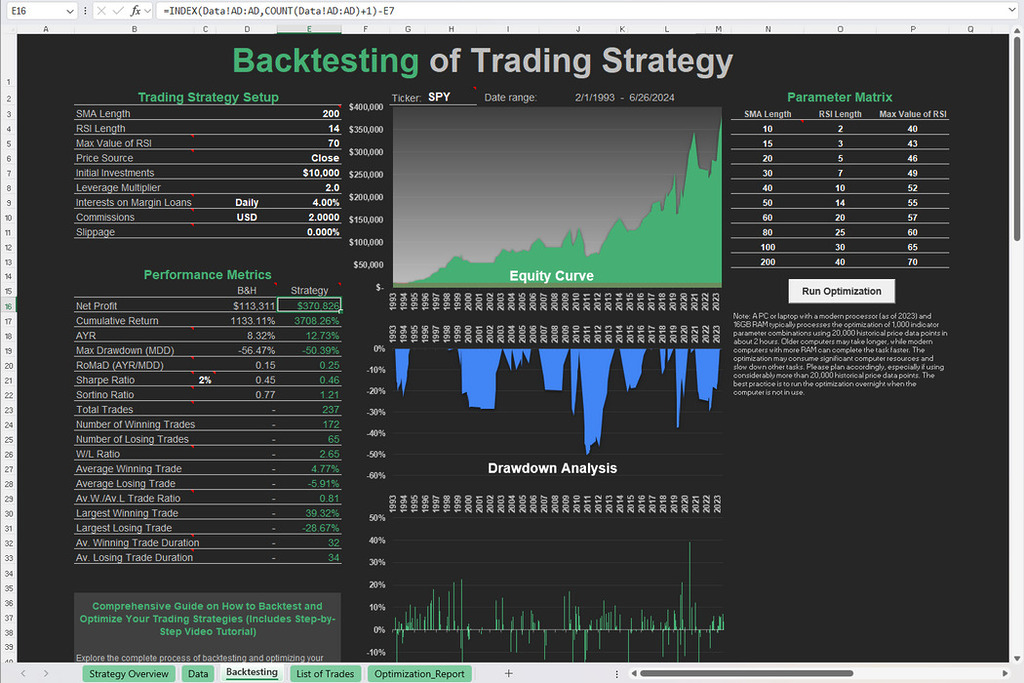
Free Backtesting Spreadsheet
Stock Market Investment Strategies
There are various stock market investment strategies that investors can employ to achieve their financial goals in the stock market. Some popular strategies include:
Buy and Hold Strategy
The buy and hold strategy involves purchasing shares of high-quality companies and holding onto them for the long term, regardless of short-term market fluctuations. The primary goal of this strategy is to benefit from the company’s growth over time and minimize trading costs and taxes. Investors who adopt the buy and hold approach focus on fundamental analysis to identify companies with strong competitive advantages, solid financials, and promising growth prospects. Examples of companies suitable for the buy and hold strategy include established blue-chip stocks like Apple Inc. (AAPL), Microsoft Corporation (MSFT), and Johnson & Johnson (JNJ).
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging is a strategy where investors invest a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. By purchasing more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high, investors can average out the cost of their investments over time. This approach helps smooth out the impact of market volatility and can result in a lower average cost per share. Dollar-cost averaging is particularly suitable for long-term investors looking to build wealth gradually over time without trying to time the market.
Value Investing
Value investing is a strategy popularized by legendary investor Benjamin Graham and later refined by Warren Buffett. Value investors seek out stocks that are trading at a discount to their intrinsic value, based on factors such as low price-to-earnings ratios, high dividend yields, or favorable growth prospects. These investors believe that the market sometimes undervalues certain stocks, presenting opportunities for long-term capital appreciation. Examples of value stocks suitable for this strategy include companies like Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (BRK.A / BRK.B), Exxon Mobil Corporation (XOM), and AT&T Inc. (T).
Growth Investing
Growth investing involves focusing on companies that are experiencing rapid earnings growth and have the potential for above-average returns. Growth investors are willing to pay a premium for these stocks in anticipation of future growth prospects. These investors typically look for companies with innovative products or services, expanding market opportunities, and strong competitive positions. Examples of growth stocks suitable for this strategy include companies like Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN), Tesla, Inc. (TSLA), and Shopify Inc. (SHOP).
Dividend Investing
Dividend investing prioritizes stocks that pay regular dividends to shareholders, providing a steady income stream. Dividend investors typically seek out companies with a history of consistently increasing dividends, strong cash flow generation, and sustainable payout ratios. These investors may reinvest dividends to compound their returns or use them as a source of passive income. Examples of dividend stocks suitable for this strategy include companies like Johnson & Johnson (JNJ), The Procter & Gamble Company (PG), and Verizon Communications Inc. (VZ).
Sector Rotation
Sector rotation is a strategy that involves shifting stock market investments among different sectors of the economy based on economic and market conditions. This strategy aims to capitalize on the relative strength of different sectors at different stages of the economic cycle. For example, during periods of economic expansion, sectors like technology, consumer discretionary, and industrials may outperform, while defensive sectors like utilities and consumer staples may perform better during economic downturns. Sector rotation requires active monitoring of economic indicators and market trends to identify opportunities for portfolio reallocation.
Growth at a Reasonable Price (GARP)
The growth at a reasonable price (GARP) strategy combines elements of both growth and value investing. GARP investors seek out companies with strong growth potential but also trade at reasonable valuations relative to their growth prospects. These investors look for companies with sustainable earnings growth, solid management teams, and competitive advantages. By focusing on stocks that offer a balance between growth and valuation, GARP investors aim to achieve above-average returns with lower risk. Examples of companies suitable for the GARP strategy include those with consistent earnings growth and reasonable valuations, such as Facebook, Inc. (FB), Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL), and Visa Inc. (V).
These are just a few of the many investment strategies available to investors in the stock market. Each strategy has its own advantages and risks, and the most suitable approach will depend on factors such as investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. It’s essential for investors to carefully research and evaluate different strategies before deciding which ones align best with their individual financial objectives. Additionally, diversification across multiple strategies or asset classes can help reduce overall portfolio risk and enhance long-term returns.
Managing Risks of Stock Market Investments
While investing in the stock market offers the potential for high returns, it also comes with inherent risks. Some common risks investors face include:
- Market Risk. Market risk refers to the possibility of losing money due to overall market fluctuations. Factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment can all impact stock prices.
- Company Risk. Company-specific risk arises from factors that affect individual companies, such as poor management, competitive pressures, or adverse regulatory changes. Investing in a diversified portfolio of stocks can help mitigate this risk.
- Liquidity Risk. Liquidity risk refers to the possibility of not being able to sell a stock quickly and at a fair price. This risk is more pronounced in thinly traded stocks or during periods of market turmoil.
- Interest Rate Risk. Changes in interest rates can affect stock prices, particularly for companies in interest rate-sensitive sectors such as banking and real estate. Rising interest rates can increase borrowing costs and reduce consumer spending, negatively impacting corporate earnings.
- Inflation Risk. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time, reducing the real value of investment returns. Investors need to ensure that their investment returns outpace the rate of inflation to preserve their wealth.
Mitigating risks requires careful portfolio management, diversification, and a long-term investment horizon. By spreading stock market investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographical regions, investors can reduce their exposure to any single risk factor.
Potential Rewards of Stock Market Investments
Despite the risks, investing in the stock market offers the potential for significant rewards over the long term. Historically, stocks have delivered higher returns than other asset classes such as bonds or cash equivalents. By investing in a diversified portfolio of stocks and staying invested through market ups and downs, investors can benefit from:
- Capital Appreciation. As companies grow and become more profitable, their stock prices tend to rise, leading to capital gains for investors.
- Dividend Income. Many companies distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. Dividend income can provide a steady stream of cash flow, especially for retirees or those seeking passive income.
- Wealth Accumulation. Over time, the power of compounding can significantly increase the value of an investment portfolio. Reinvesting dividends and allowing stock market investments to grow over the long term can help investors accumulate wealth and achieve their financial goals.
- Hedge Against Inflation. Stocks have historically outpaced inflation, making them a potential hedge against rising prices and preserving purchasing power over time.
Final Thoughts
Investing in the stock market can be a rewarding endeavor, but it requires patience, discipline, and a thorough understanding of the risks involved. By employing sound investment strategies, managing risks effectively, and staying focused on long-term goals, investors can navigate the complexities of the stock market and unlock its potential rewards. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, the key to success lies in education, diligence, and a willingness to adapt to changing market conditions. With careful planning and prudent decision-making, anyone can build a successful investment portfolio and secure their financial future in the stock market.
Share on Social Media: